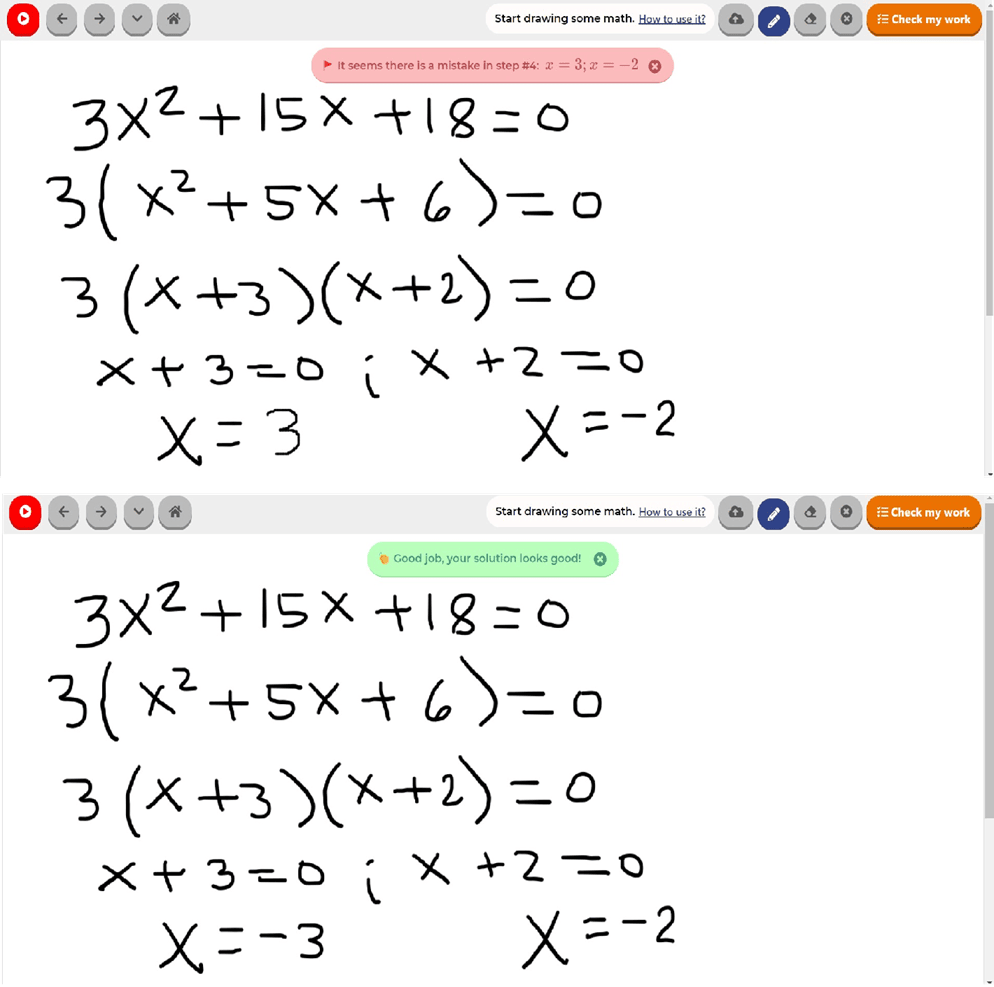
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Find the discriminant
- Integrate by partial fractions
- Product of Binomials with Common Term
- FOIL Method
- Integrate by substitution
- Integrate by parts
- Integrate using tabular integration
- Integrate by trigonometric substitution
- Weierstrass Substitution
- Prove from LHS (left-hand side)
- Load more...
Expand $\left(x^2-a^2\right)^2$