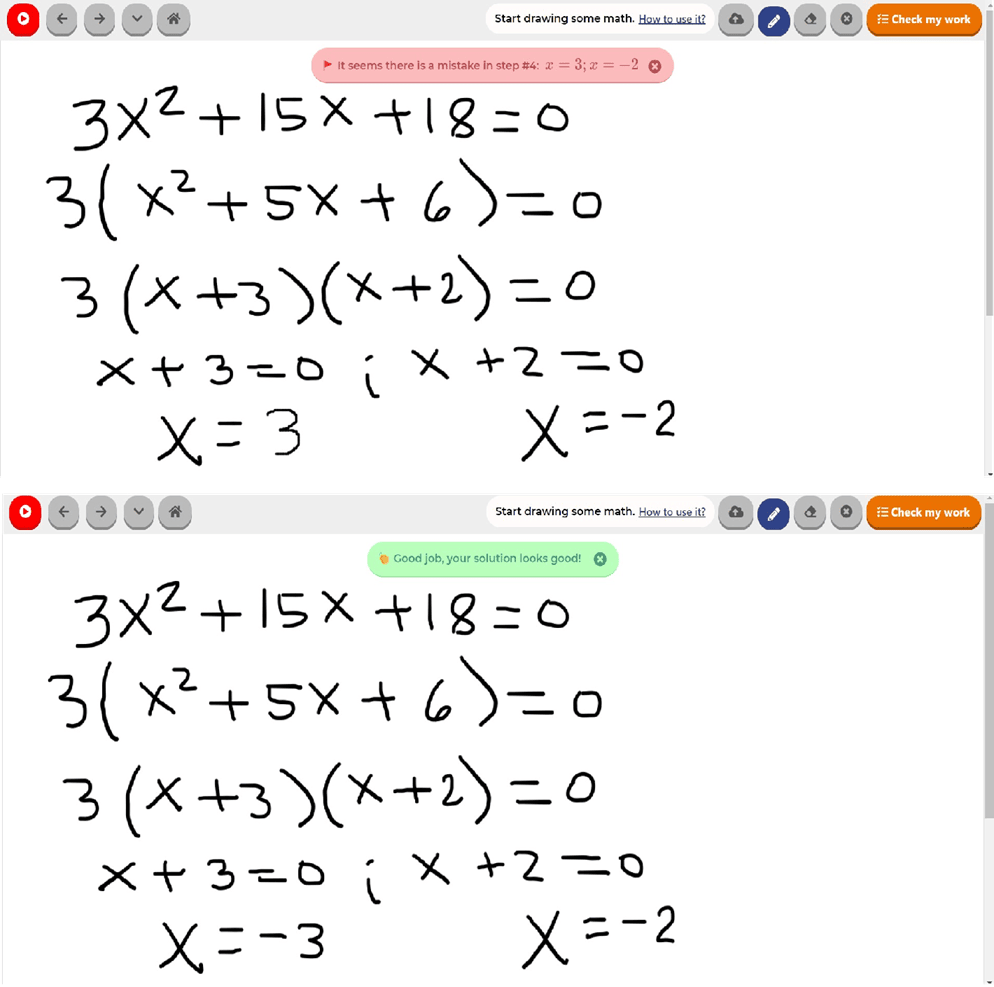
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Find the derivative
- Find the derivative using the definition
- Find the derivative using the product rule
- Find the derivative using the quotient rule
- Find the derivative using logarithmic differentiation
- Find the derivative
- Integrate by partial fractions
- Product of Binomials with Common Term
- FOIL Method
- Integrate by substitution
- Load more...
Simplifying
The derivative of the constant function ($\frac{55}{2}$) is equal to zero