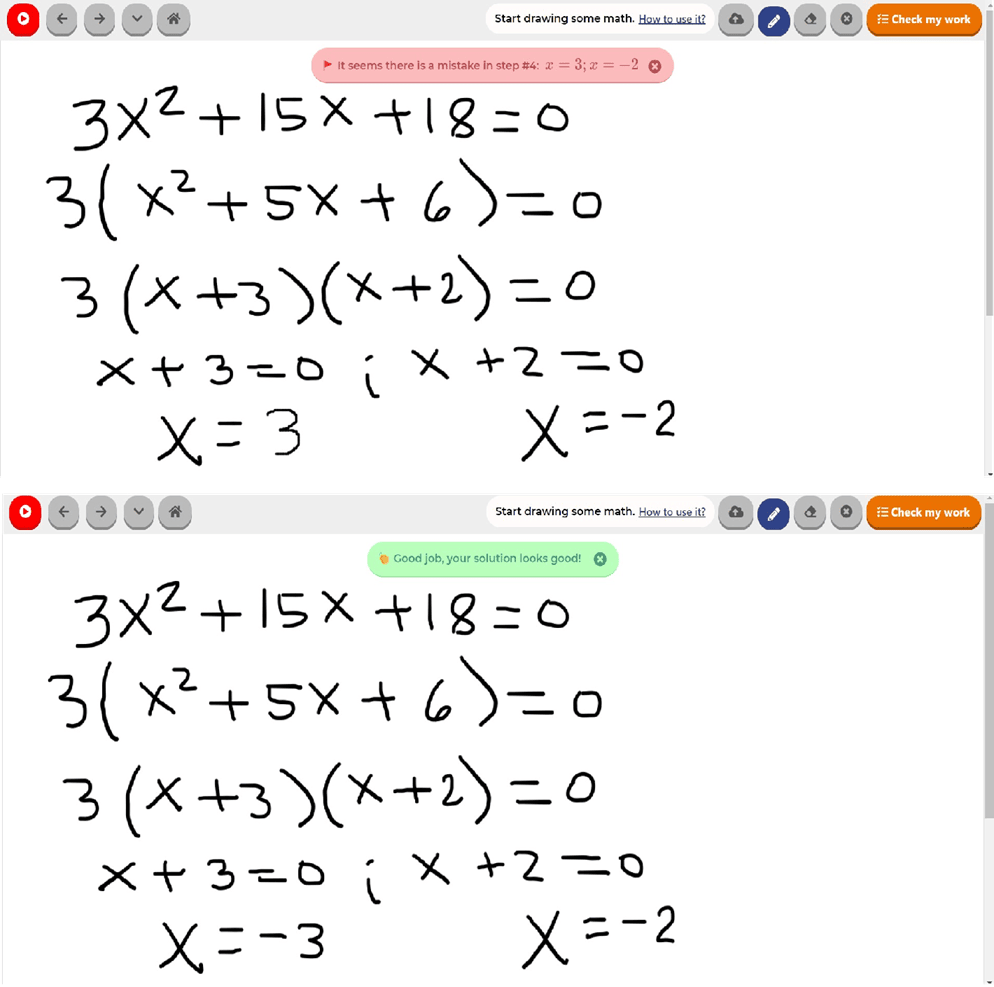
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Solve by implicit differentiation
- Find the derivative using the definition
- Exact Differential Equation
- Linear Differential Equation
- Separable Differential Equation
- Homogeneous Differential Equation
- Find the derivative using the product rule
- Find the derivative using the quotient rule
- Find the derivative using logarithmic differentiation
- Find the derivative
- Load more...
Apply implicit differentiation by taking the derivative of both sides of the equation with respect to the differentiation variable
Learn how to solve problems step by step online.
$\frac{d}{dx}\left(-2x-21\ln\left(-x+10\right)\right)=\frac{d}{dx}\left(y\right)$
Learn how to solve problems step by step online. Find the implicit derivative of -2x-21ln(-x+10)=y. Apply implicit differentiation by taking the derivative of both sides of the equation with respect to the differentiation variable. The derivative of the linear function is equal to 1. The derivative of a sum of two or more functions is the sum of the derivatives of each function. The derivative of the linear function times a constant, is equal to the constant.