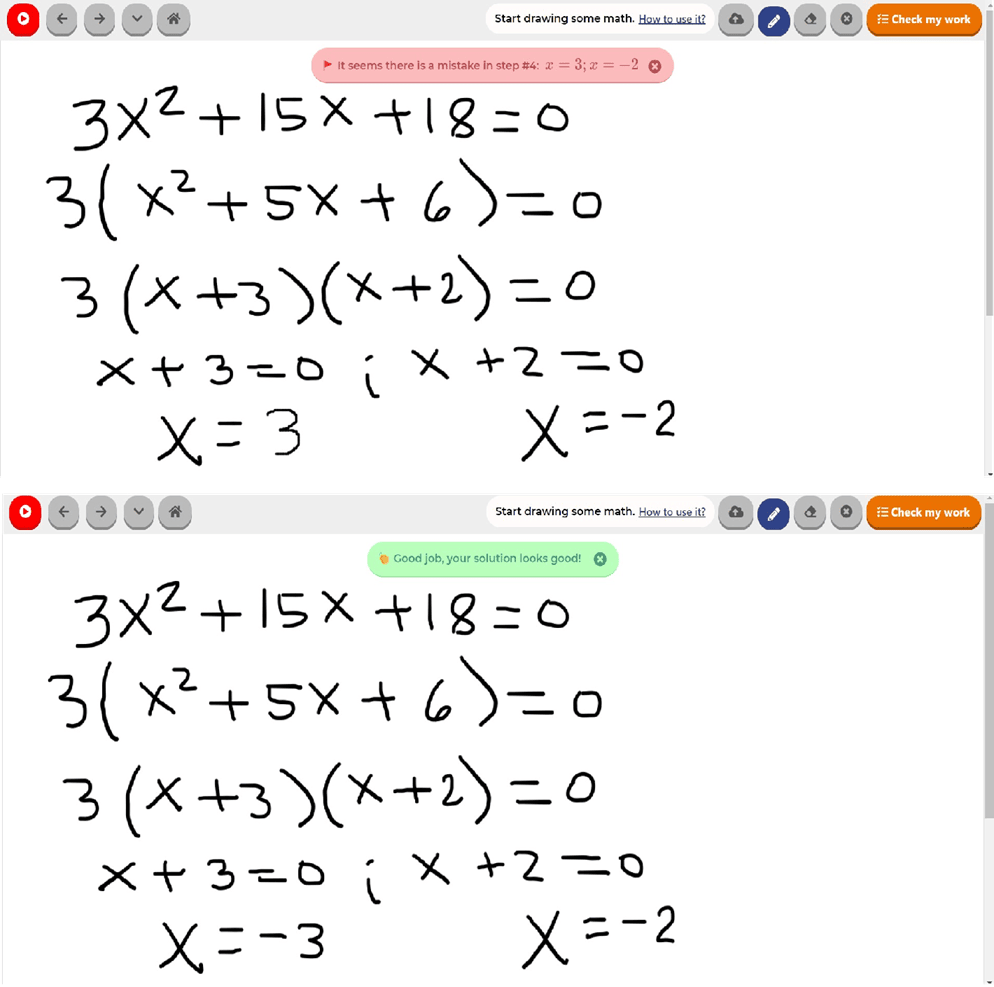
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Choose an option
- Integrate by partial fractions
- Integrate by substitution
- Integrate by parts
- Integrate using tabular integration
- Integrate by trigonometric substitution
- Weierstrass Substitution
- Integrate using trigonometric identities
- Integrate using basic integrals
- Product of Binomials with Common Term
- Load more...
Rewrite the expression $\frac{x}{x^2-1}$ inside the integral in factored form
Rewrite the fraction $\frac{x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}$ in $2$ simpler fractions using partial fraction decomposition
Expand the integral $\int\left(\frac{1}{2\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{2\left(x-1\right)}\right)dx$ into $2$ integrals using the sum rule for integrals, to then solve each integral separately
The integral $\int\frac{1}{2\left(x+1\right)}dx$ results in: $\frac{1}{2}\ln\left(x+1\right)$
The integral $\int\frac{1}{2\left(x-1\right)}dx$ results in: $\frac{1}{2}\ln\left(x-1\right)$
Gather the results of all integrals
As the integral that we are solving is an indefinite integral, when we finish integrating we must add the constant of integration $C$